Hafnium Element
Hafnium is a chemical element or silvery-white transition metal of Group 4 (IVB) of the periodic table with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. It is used to make control rods in nuclear power plants due to its neutron absorbance. The metal hafnium remained undiscovered till 1923 and was first discovered in zirconium mineral zircon by Dutch physicist Dirk Coster and the Hungarian chemist George Charles von Hevesy in 1923. Niels Bohr convincingly advised Coster and Hevesy to look for the element with the atomic number 72. In honor of Bohr, the element hafnium was named after his native land Copenhagen whose old name was Hafnia. Elemental hafnium was obtained by sodium reduction of its mineral. It was separated from zirconium by repeated crystallization. However, the pure metal was made in 1925 by decomposing hafnium tetra-iodide over a hot tungsten wire.
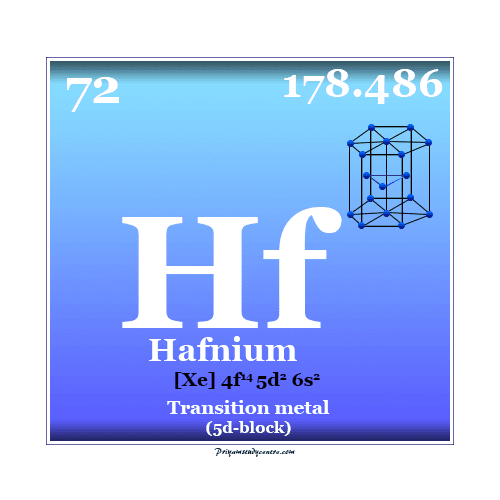
Properties of Hafnium
It is a silvery-white, high-melting, hard metal that is fairly electropositive. The most common and stable oxidation number or state of the metal is +4. In lower oxidation states, it is strongly reducing in nature which reduces water molecules. Hence it has no aqueous chemistry in lower oxidation states.
| Properties of Hafnium |
|||
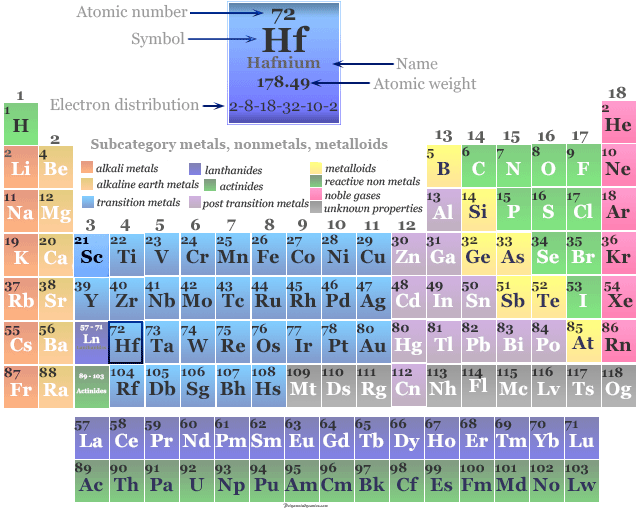
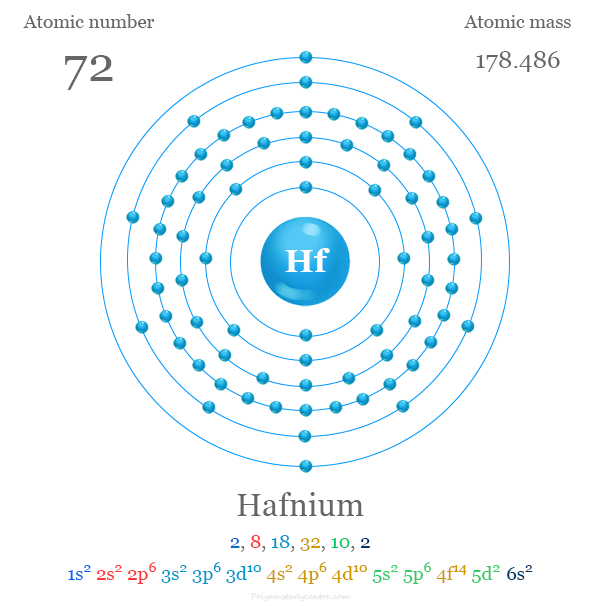
| Atomic number | 72 | ||
| Electron per shell | 2, 8, 18, 32, 10, 2 | ||
| Electronic configuration | [Xe] 4f14 5d2 6s2 | ||
| Block | d-block | ||
| Period | period 6 | ||
| Group | group 4 | ||
| Atomic weight | 178.486 | ||
| Melting point | 2506 K (2233 °C, 4051 °F) | ||
| Boiling point | 4876 K (4603 °C, 8317 °F) | ||
| Crystal structure | hexagonal close-packed (hcp) | ||
| Density | 13.31 g/cm3 | ||
| Molar heat capacity | 25.73 J mol−1K−1 | ||
| Electrical resistivity | 331 nΩ·m | ||
| Atomic radius | 159 pm | ||
| Covalent radius | 175±10 pm | ||
| Chemical properties | |||
| Oxidation number | +4 | ||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 1.3 | ||
| Ionization energy (kJ/mol) | 1st | 2nd | 3rd |
| 658.5 | 1440 | 2250 | |
Where is Hafnium Found?
The metal was undiscovered till 1923. After 130 years the metal was discovered in zirconium mineral zircon. It occurs in nature at a much lower rank about 2.8 ppm.
Isotopes
Hafnium contains 34 isotopes with an atomic mass of 153 to 186. The different types of radioactive isotopes of the metal are obtained by nuclear reaction. The half-life of radioactive isotopes is very small about 400 milliseconds.
Separation of Zirconium and Hafnium
Zircon carries about 0.5 to 2 percent hafnium. Both metals have the same atomic and ionic radii. Their charge by radius ratio is also the same.
The chemistry of these two transition metals is very similar. Therefore, no straightforward chemical methods can be derived for their separation or individual extraction. The hope lies in some slight differences in the solubility of their compounds.
Fractional Crystallization of Double Fluoride
The solubilities of (NH4)2[ZrF6] and (NH4)[HfF6] in water are 0.611 and 0.891 moles/liter at 0°C. Therefore, it is possible to separate these two compounds by repeated crystallization.
Elution of the Metal Tetrachloride
Anhydrous methanol solution of tetrachloride is passed through a silica gel column. The fixed chlorides were then eluted first with 2N hydrochloric acid in methanol. It removes zirconium chloride. Finally, elution is carried out with 7N sulfuric acid which removes hafnium.
Chemical Compounds
Group 4 contains the transition metals like titanium, zirconium, and hafnium. In the past, Th can be included in the place of Hf. But now, thorium goes to f block elements with actinides.
All the elements possess a d2s2 electronic configuration outside the noble gas core. The stable and most common oxidation number of these metals is +4. The lower oxidation states become increasingly unstable with the increasing atomic number. Zirconium (0) and hafnium (0) are known mostly in organometallic compounds.
The chemistry or chemical properties of zirconium and hafnium are very similar. Generally, it forms a hexagonal close-packed crystal lattice.
Due to zirconium impurities, the properties of hafnium are widely influenced by the zirconium atom. The sizes of Zr and Hf are very similar due to the lanthanide types of construction in the Hafnium atom.
Hafnium Oxide
The dioxide HfO2 is a high melting solid (mp – 2900 °C). It is insoluble in water or cold dilute acid except for HF. The oxide reacts slowly with acid when heated for a long time.
No definite hydroxide of group-4 elements is known. The hydroxides are readily hydrated oxides. The acidity of hydrated oxides falls in the order Ti > Zr > Hf.
Hafnium Halides
The tetrahalides of Ti, Zr, and Hf are formed by covalent bonding with halogens. Therefore, they are non-electrolyte in nature and soluble in organic solvents. In the vapor state, these are monomeric and tetrahedral. The extent of hydrolysis decreases from Ti to Hf.
TiX4 compounds are hydrolyzed to give TiO2 in water. The compounds ZrX4 and HfX4 give ZrX2O and HfX2O in water.
Uses of Hafnium
- Hafnium is a good absorber of neutrons and is used for making control rods in nuclear power reactors.
- Sometimes, it is used in the filament of incandescent lamps and cathode tubes.
- Due to the very high melting point, hafnium metals are used in plasma welding torches. It is also used in rectifiers.
- The metal is alloyed with other metals like iron, titanium, niobium, and tantalum. The alloyed metal is used for the production of liquid rocket thruster nozzles.
- It is used as a scavenger in the steel industry due to its good affinity toward oxygen and nitrogen. Thus, it removes dissolved oxygen and nitrogen.
- Hafnium chemical catalyst is used in the polymerization reaction of organic compounds.