Acetylene Gas
Acetylene or ethyne is a colorless gas with the general chemical formula C2H2. When acetylene gas combustion with oxygen it forms a luminous smoky flame due to the high carbon materials. The gas is used in oxy-acetylene torches, oxy-acetylene blowpipes for cutting metals, or welding equipment. Acetylene gas is also used for the preparation of a large number of organic compounds like acetaldehyde (CH3CHO), ethyl alcohol (C2H5OH), and acetic acid (CH3COOH). The compressed or liquified unsaturated hydrocarbon acetylene is a highly explosive gas. Therefore, acetylene gas is stored with acetone solution under 10 atm pressure because acetone absorbs some porous materials for setting the safety of the cylinder or supplier tank.
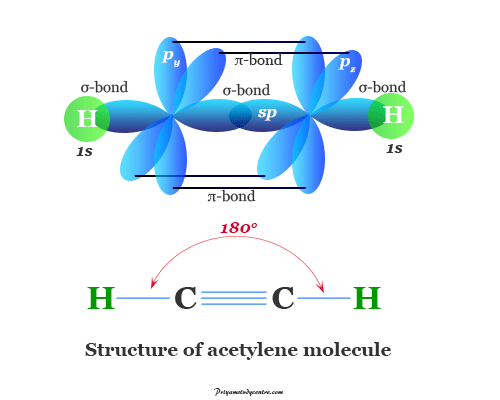
Lewis structure of acetylene
The Lewis structure of the acetylene setup by one triple bond is known as the acetylenic chemical bond. The infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum of ethylene compounds depends on whether they contain acetylenic hydrogen or not.
In RC≡CH, one region has a frequency of 3310-3300 cm−1 due to the ≡C-H stretch, and another region has a frequency of 2140-2100 cm−1 due to the C≡C stretch.
Preparation Process
The gas is generally prepared by creaking methane or ethane mixture. Heating a mixture of ethane or propane with the stream at about 1000-1300 °C temperature. Natural gas or hydrocarbons are also used as the starting material for the preparation of C2H2.
Acetylene from calcium carbide
Acetylene is an important member of the alkyne that is prepared industrially by the action of water on calcium carbide.
Other methods for the preparation of the alkynes in learning chemistry are,
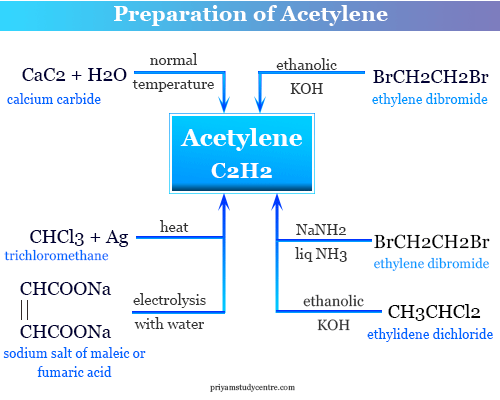
Acetylene from dicarboxylic acid
The gas can be produced during the electrolysis of the concentrated sodium or potassium salt of the maleic or formic acid solution by the Kolbe method.
Acetylene from ethylene dibromide
Ethylene is also prepared by the action of ethanolic potassium hydroxide on ethyl bromide solution. The reaction process is in two steps.
- Under suitable conditions, the intermediate vinyl bromide also is isolated.
- Sodamide in liquid ammonia is used instead of ethanolic potassium hydroxide in the acetylene preparation process. Since there is less tendency to form by-products.
Properties of C2H2
| Acetylene | |
| Chemical formula | C2H2 |
| Molar mass | 26.038 g mol−1 |
| Molecular shape | Linear structure |
| Appearance | Colorless gaseous hydrocarbon |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | 1.1772 g/L |
| Melting point | −80.8 °C |
| Solubility | Slightly soluble in water or alcohol and soluble in acetone and benzene |
| Conjugate acid | Ethynium |
| Heat capacity | 44.036 J mol−1 K−1 |
| Entropy | 200.927 J mol−1 K−1 |
| Gibbs free energy (ΔfG˚) | 209.879 kJ mol−1 |
| CAS Number | 74-86-2 |
Owing to the presence of a triple bond, it is more unsaturated hydrocarbon than ethylene. It formed addition products with two or four univalent atoms or groups. The triple bond consists of one sigma and two pi-bonds to form a linear molecule.
When two univalent atoms add to the triple bond, the diagonal arrangement changes into the trigonal or tetrahedral arrangement. Therefore, under suitable conditions, ethylene gas uses to isolate the intermediate alkene or olefins like ethylene with a trigonal structural formula.
CH≡CH adds to the hydrogen atom in the presence of the chemical catalyst. The reaction process in the two stages by the preparation of alkenes and alkanes.
We use a suitable catalyst like Lindlar’s catalyst for the conversion of alkyne to an alkene. Lindlar’s catalyst consists of Pd-CaCO3 partially poisoned with lead acetate. The better catalyst for the conversion of alkyne to an alkene is Pd- BaSO4 partially poisoned with quinoline.
Uses of acetylene
- The gas is not only used in an oxy-acetylene torch or welding material setup.
- It is also used for the synthesis of many organic compounds like alcohol, ether, and carboxylic acids.
- In the chemical industry, for the preparation of synthetic rubber and plastic bottles, we used C2H2.
- Acetylene gas is added to hydrogen cyanide in the presence of a cuprous chloride catalyst to form vinyl cyanides. It is used for the manufacture of Buna synthetic rubber. This is the copolymer of vinyl cyanide and butadiene.
- Vinyl cyanide is also prepared by passing the mixture of ammonia, steam, and air over the catalyst like oxide of the chemical elements molybdenum or cobalt.
- Vinyl acetate compounds in chemistry are manufactured by passing the mixture of C2H2 and CH3COOH vapor over zinc acetate on charcoal at about 170°C. This acetylene compound is used in the plastic industry for making plastic bottles and toys.