Sodium
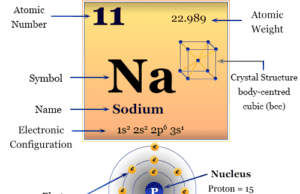
Sodium Chemical Element
Sodium is a soft, low melting, silvery white alkali metal or chemical element of Group 1 or IA of the periodic table with...
Magnesium
Magnesium Element
Magnesium is a chemical element, alkaline earth metal of Group 2 (IIA) of the periodic table with the symbol Mg and atomic number...
Beryllium
Beryllium Element
Beryllium is a chemical element or alkaline-earth metal of Group 2 (IIA) of the periodic table with the symbol Be and atomic number...
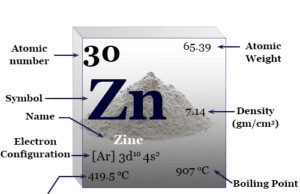
Zinc
Zinc Metal
Zinc is a chemical element or silvery lustrous metal of Group 12 or IIB of the periodic table with atomic number 30 and...
Nickel
Nickel Metal
Nickel is a chemical element, silvery, malleable, ductile, ferromagnetic transition metal of group 10 of the periodic table with atomic number 28 and symbol...
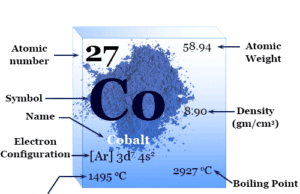
Cobalt
Cobalt Metal
Cobalt is a chemical element, lustrous silvery-gray ferromagnetic transition metal of Group 9 (VIIIB) of the periodic table with atomic number 27 and...
Manganese
Manganese Chemical Element
Manganese is a chemical element or a greyish-white hard, brittle paramagnetic transition metal of Group 7 (VIIB) of the periodic table with the...
Steel
Different Types of Steel
Steel is essentially a refined alloy of iron that contains a lower percentage of carbon, silicon, and other metals to improve...
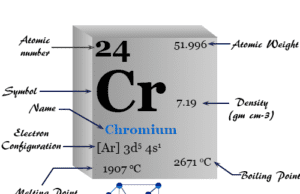
Chromium
Chromium Metal
Chromium is a chemical element or hard, malleable, greyish-white shiny transition metal of Group 6 (VIB) of the periodic table with atomic number...
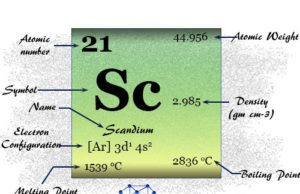
Scandium
Scandium Element
Scandium is a chemical element or transition metal of Group 3 of the periodic table with atomic number 21 and symbol Sc. The...