Reverse Osmosis Water Filtration System
Reverse osmosis (RO) system is a multi-stage water filtration process that removes contaminants from unfiltered or feed water when pressure forces it through a semipermeable membrane. A reverse osmosis machine or unit uses to filter or separate ions, unwanted molecules, and larger particles from unfiltered or feed water to produce pure drinking water by a semi-permeable RO membrane. The working process of a reverse osmosis system is carried out by applying pressure to overcome osmotic pressure that favors the flow of solvent from a low concentration side to a high concentration side. Reverse osmosis filters work by using a high-pressure pump to increase the pressure of the solution side and retain the small sized solutes on the pressurized side of the semipermeable membrane.
The amount of pressure needed to overcome osmotic pressure depends on the concentration of the salt in the unfiltered or fed water. Therefore, for highly concentrated contaminated water, high pressure is needed to overcome osmotic pressure.
Reverse osmosis is the most popular and older water purification technology that is very useful for removing salts and other pollutants from unfiltered or feed water by semipermeable membranes. It can be used to remove dissolved or suspended chemical species such as salts (ions), colloid particles, small organic molecules, bacteria, and pyrogens from water.
Reverse osmosis is an expensive water filtration system because it needs periodic replacement of RO membranes. Lots of energy is also required for the filtration of water. The lifespan of the RO membrane is comparatively short for hard water. A large amount of water can also be wasted during the purification by reverse osmosis.
Osmosis and Reverse Osmosis
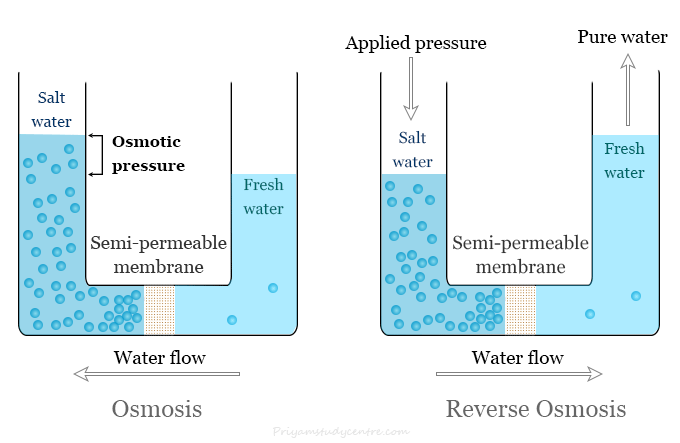
Reverse osmosis is one of the oldest and a most popular water filtration technique or system that work opposite to osmosis. Osmosis refers to the movement of solvent mostly water through a semipermeable membrane. The flow of solvent in osmosis occurs from a solution of low concentration to a solution of high concentration. The semipermeable membrane is a membrane that is permeable to the solvent and not to the solute.
On the other hand, reverse osmosis is a process where osmosis occurs in reverse. Osmosis occurs naturally without requiring any energy but we apply energy to reverse the natural osmosis process.
Osmosis
A naturally occurring phenomenon that occurs when two solutions with different concentrations are separated by a semipermeable membrane is called osmosis. The semipermeable membrane is expected to be permeable to the solvent and not to the solute.
In the natural osmosis process, a solvent will migrate from a low solute concentration (high potential) to a high solute concentration (low potential). For example, osmosis occurs when plant roots absorb water from the soil and our kidneys absorb water from our blood.
The reduction in the Gibbs free energy of the system is the driving force for the movement of the solvent. Osmotic pressure is generated due to the movement of solvent from lower to higher concentration regions.
Osmotic Pressure
The excess pressure that must be applied to the solution to prevent the passage of solvent into the solution is called osmotic pressure. It is a colligative property. Therefore, it depends on the number of solute particles but not their nature. It is directly proportional to the concentration or number of solute molecules or ions.
In a unit mass, low molecular weight substances (sodium chloride, glucose) will have more molecules compared to the high molecular weight substances (albumin, globulin). Therefore, the substances with low molecular weight exhibit greater osmotic pressure.
Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water purification process that eliminates impurities from unfiltered water or feed water. It uses pressure to force unfiltered water through a semipermeable membrane.
Applying an external pressure to reverse the natural flow of pure solvent is called reverse osmosis. In an RO water purification system, excess pressure is applied to the contaminated water side for the movement of pure water through a semipermeable membrane.
Reverse Osmosis Membrane
A reverse osmosis membrane is an important unit in an RO machine that helps to remove salts and other pollutants from drinking water. These RO membranes are usually made of cellulose acetates, polyamides, polyimides, and poly-sulfones. After the development of polymer technology, various efficient membranes were developed and used in various RO machines.
The RO membrane should not allow large molecules or ions through the pores or holes. However, it should allow smaller components of the solution such as solvent or water molecules. A membrane in a reverse osmosis system works on the basis of the molecular size and ionic charge of the impurities.
Any impurities having a molecular weight greater than 200 Da are not allowed to pass through the RO membrane. The elements having low ionic change and non-ionic species like carbon dioxide are easily passed through RO membranes.
Osmosis membranes are sensitive to changes in the pH of water. Small concentrations of oxidized substances such as chlorine and chlorine dioxide, various organic compounds, algae, and bacteria can change the pH level of water. Therefore, when the water pressure drives water across the RO membrane, additional filters such as sediment or carbon filters used to remove contaminants are filtered out. Careful pretreatment is always needed in order to decrease RO membrane contamination and fouling.
How Reverse Osmosis Works?
In chemistry, osmosis is the process by which water passes through a semi-permeable membrane from a less concentrated solution into a more concentrated one. Reverse osmosis works by using a high-pressure pump to increase the pressure of the solution side and retain the small size solutes on the pressurized side of the semipermeable membrane.
A semipermeable membrane in a reverse osmosis system works on the basis of the molecular size and ionic charge of the impurities. Reverse osmosis can purify water by retaining the solute on the pressurized side of the membrane and the purified water passes to the other side.
In the natural osmosis process, a solvent will migrate from a high water potential to a low water potential. Reverse osmosis is one of the oldest and most popular water purification techniques that work opposite to osmosis.
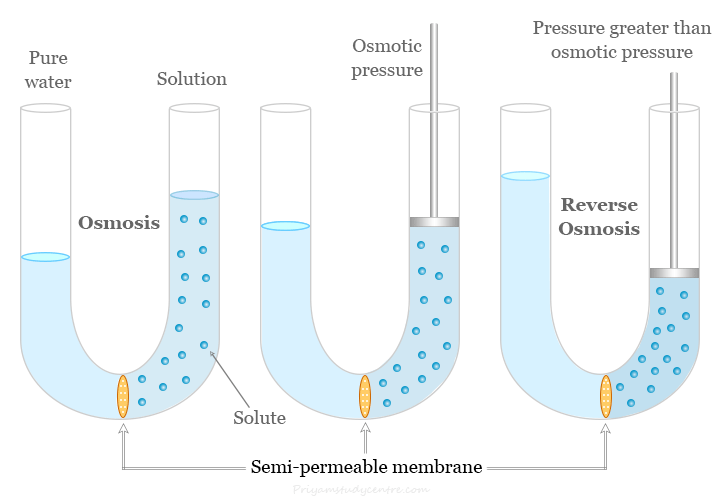
Reverse osmosis occurs when we use external pressure to run the osmosis process in the reverse direction. Therefore, it filters the contaminated or saline water to produce pure water. RO can used mainly to remove dissolved or suspended chemical species such as salts (ions), colloid particles, small organic molecules, bacteria, and pyrogens from contaminated water.
Reverse Osmosis System for Home
A household water filtration system uses a reverse osmosis step for the purification of drinking water. Such water-purifying systems contain sediment filters, activated carbon filters, RO membranes, and ultraviolet lamps. Household drinking water purification systems commonly work by four stages of filtration including a RO step,
- Sediment filter: A sediment filter uses to trap different types of sediments or suspended solids including rust and calcium carbonate.
- Pre-carbon block: An activated carbon filter traps organic chemicals and chlorine before forcing unfiltered water through a semipermeable membrane to remove dissolved solids. Therefore, it helps to increase the life of the RO membrane used for filtration.
- Reverse osmosis membrane: The RO membrane can trap molecules heavier than water. Therefore, it removes sodium, calcium, high levels of lead, mercury and arsenic, various minerals, fluoride, chloride, sulfate, etc.
- Ultraviolet Lamps: An ultraviolet lamp is used to kill harmful bacteria and pyrogens that are not removed by the RO membrane.
Uses of Reverse Osmosis
The reverse osmosis system is used mainly around the world for the filtration of water for industrial, residential, commercial, and scientific purposes. The RO system collects and purifies wastewater for irrigation and drinking. It also removes minerals from water used in the boiler of power plants.
A solar-powered desalination unit uses solar energy for the filtration of water by reverse osmosis process. Using such a distillation unit reduces electricity costs and greenhouse gas emissions.
The RO systems may be used to remove many types of dissolved and suspended chemical species and bacteria from contaminated water. In household production, it uses as a source of potable drinking water. The most common uses of the RO process are given below,
Water Purification System
- We use the reverse osmosis step in a household drinking water purification system to improve the quality of drinking and cooking water.
- Portable RO water purifiers are sold and used for personal water purification in various locations of the world.
- RO step is also used to remove pollutants and microorganisms in the production of bottled mineral water.
- RO system can be used to produce deionized water for chemical laboratories.
Uses in Power Plants
RO process is applied for the purification of water stored in drains and used in boilers of power plants. The RO water does not leave any deposits on the machinery used in power plants. It also helps to reduce corrosion caused by to oxidation of metals.
The deposits inside or outside the boiler may reduce its efficiency and result in poor steam production. Therefore, it decreases the production of electricity at the turbine.
Food Industry
In the food industry, the reverse osmosis process is used for concentrating liquid food products such as fruit juices. RO technology uses in the food industry due to its lower operation cost. It is also used in the food industry to avoid conventional heat-treatment processes. Heat may destroy various heat-sensitive substances such as proteins and enzymes present in food products.
In the dairy industry, it is extensively used for the production of whey protein powders. It also reduces shipping costs by concentrated milk.
In the wine production process, RO is also used for concentrating alcohol that is used for making wine.
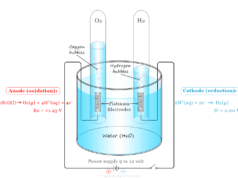
Hydrogen Production
In the small-scale hydrogen production process, RO is used for the purification of water that is used in electrolysis. The pure water helps to prevent mineral deposition on the surface of the electrode.
Benefits of Reverse Osmosis System
- The reverse osmosis water filtration system has the ability to remove most of the total dissolved solids (TDS) in water. Therefore, it improves the odor, appearance, and overall taste of your drinking water.
- Cooking with pure water obtained from the RO system dramatically impacts the flavor of food items such as coffee, tea, soup, etc.
- It is the best and most useful method for softening your drinking water.
- High-quality filtration of the RO systems can remove bacteria or heavy metals from your drinking water.
- The energy used by RO systems for water filtration is relatively low compared to other similar systems.
- RO is space saving system, thus you can install it in a small space in the kitchen or dining room.
- The maintenance of the RO system is very simple but costly.
- It is a totally automatic system and is designed to start and stop on its own.
Disadvantages of Reverse Osmosis System
- The reverse system removes healthy minerals such as calcium, magnesium, potassium, and sodium bicarbonate from drinking water. Therefore, it may impact our overall health.
- The RO system which we use in our home wastes a huge amount of water.
- RO is an expensive process because it requires periodic maintenance with slow output.
- The installation of an RO system in our home is costly.
- The filter replacement cost of the RO system is very expensive.
- The membranes used in the RO machine have limited pH and temperature tolerance.
- The RO membranes can be degraded at temperatures greater than 35°C.
- Reverse osmosis membranes may also be degraded by chlorine that is present in water which we filter by the RO filtration system. Therefore, we need additional filters such as sediment and carbon filters.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is reverse osmosis?
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water filtration system that eliminates impurities from unfiltered water or feed water by using pressure to force water through a semipermeable membrane.
How do reverse osmosis water filters work?
Reverse osmosis filters work by using a high-pressure pump to increase the pressure of the solution side and retain the small size solutes on the pressurized side of the semipermeable membrane. RO can used to remove dissolved or suspended chemical species such as salts (ions), colloid particles, small organic molecules, bacteria, and pyrogens from water.
What is a reverse osmosis system?
A reverse osmosis system is a multi-stage water filtration process that removes contaminants from unfiltered water, or feed water, when pressure forces it through a semipermeable membrane. The RO system effectively eliminates dissolved salts (ions), colloid particles, small organic molecules, bacteria, and pyrogens.
Is reverse osmosis water good for you?
Yes, a reverse osmosis water filtration system is good for you because it eliminates dissolved salts (ions), colloid particles, small organic molecules, bacteria, and pyrogens. However, it also removes many essential minerals that are good for our health. Moreover, RO water is safe for drinking and cooking.
Why is reverse osmosis expensive?
Reverse osmosis is an expensive water filtration system because it needs periodic replacement of RO membranes and lots of energy required for the filtration of water. The lifespan of the RO membrane is comparatively short for hard water. It also wastes a large amount of water.