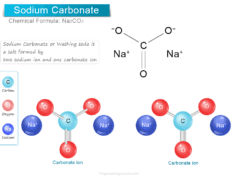
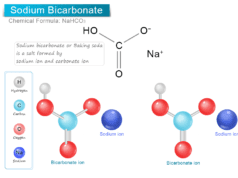
Boric Acid Powder
Boric acid or Boric Powder, also called hydrogen borate or orthoboric acid is a white crystalline solid with the chemical formula of H3BO3 or B(OH)3. In chemistry, boric acid powder is a weak acid that is formed by boron, oxygen, and hydrogen. Boric powder is commonly prepared by acidifying and heating borax solution. Boric acid is found in minerals and volcanic water or the end product of hydrolysis of boron halides or hydrides. It is commonly used as an antiseptic in medicine, insecticide in agriculture, and neutron absorber in the nuclear power generation process.
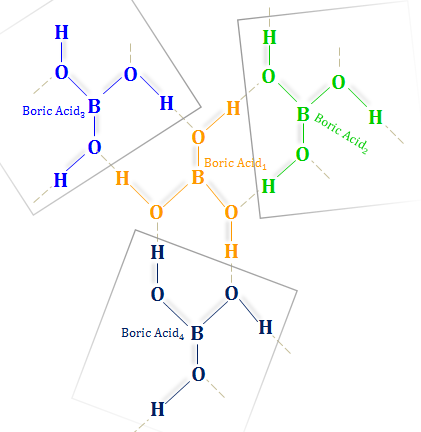
Boric Acid Structure
The shining white polymeric crystal structure of boric acid contains B(OH)3 units linked with infinite hexagonal layers due to hydrogen bonding.
Each acid molecule contains a boron-hydrogen chemical bond. The boron atom is the central atom (sp2 hybridized) with three hydroxyl groups. The overall molecular geometry of H3BO3 is the trigonal planner.
Boric Acid Preparation
Boric acid is commonly obtained by boiling borax with acids and then crystallizing it.
Na2B4O7(OH)4 + 2 HCl + 3 H2O → 4 H3BO3 + 2 NaCl
BCl3 + 3 H2O → H3BO3 + 3 HCl
H3BO3 can also be prepared by hydrolysis of diborane and boron trihalides (boron trichloride or boron tribromide).
B2H6 + 6 H2O → 2 H3BO3 + 6 H2
BCl3 + 3 H2O → H3BO3 + 3 HCl
Properties of Boric Acid
| Properties | |
| IUPAC name | Boric acid |
| CAS Number | 10043-35-3 |
| Chemical formula | H3BO3 or B(OH)3 |
| Molar mass | 61.83 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid powder |
| Density | 1.435 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 170.9 °C |
| Boiling point | 300 °C |
| Solubility | Soluble in water but moderately soluble in pyridine and very slightly soluble in acetone |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.24 |
| Conjugate base | Borate |
Acidity of Boric Acid
The water solution of the boric acid molecule shows weak acid properties (pH scale = 9.2). It does not use hydrogen ions to show an acidic character. Therefore, H3BO3 is a Lewis acid that accepts electron pairs from the hydroxyl ion. When orthoboric acid is dissolved in water, it partially dissociates to give metaboric acid.
H3BO3 ⇌ HBO2 + H2O
The solution is mildly acidic because orthoboric acid and metabolic acid mildly ionize in the water solution.
H3BO3 + H2O ⇌ [H2BO3]− + H3O+
HBO2 + H2O ⇌ [BO2]− + H3O+
The conductance in an aqueous solution of H3BO3 is very weak. The conductivity of the solution can be enhanced by the addition of alcohol like ethanol, methanol, glycerol, etc.
For acid base titration, we added alcohol to increase acidity and then titrated it with a base solution using phenolphthalein as an indicator. Such a type of reaction is the basis of the borax phenolphthalein test of glycerol in learning chemistry.
Chemical Properties of H3BO3
Dilute aqueous boric acid solution contains mononuclear compounds but various polymeric ions formed in concentrated chemical solution depending on the pH, concentration, and temperature
- At 100°C, the acid changed to metaboric acid (HBO2).
- At 140°C to pyroboric acid.
- Finally, at a higher temperature, it is converted to boron trioxide (B2O3).
Chemical Reactions
H3BO3 generally reacts with ethyl alcohol or ethanol in the presence of sulfuric acid to form alkyl or ethyl borate.
H3BO3 + 3 CH3CH2OH → B(OCH2CH3)3 + 3 H2O
Alkyl or ethyl borate is used for quantitative chemical analysis of borates.
On fusion with metal oxides colored borate glasses are formed. On fusion with NH4HF2 ultimately BF3 is obtained. It acts as a strong acid in anhydrous sulfuric or nitric acid solution.
The reaction of H3BO3 with sodium peroxide or hydrogen peroxide gives sodium or mono peroxo-borates. The structure of the peroxoborate ion, [B2(O2)2(OH)4]−2 contains sp3 hybridized boron atoms. The tetrahedral sp3 hybridized orbitals of boron are linked by bridging μ-peroxo groups.
Boric Acid Powder Uses
- Boron and orthoboric acid are extensively used in the modern age reinforcement materials in space shuttles, aircraft, and the textile industry. H3BO3 is also important for making borosilicate glasses.
- For the preparation of enamels of our teeth, we generally use shining of H3BO3 and borax powder.
- For over a hundred years, orthoboric acid has been used for the treatment of vaginal suppositories or infections.
- In medicinal science, orthoboric acid is mostly used by physicians and patients as an antiseptic, antibacterial, or treatment of candidiasis and BV.
- Sodium perborate which is prepared from H3BO3 used for detergent preparation in the chemical industry.
- Boron carbides and metal borides are extensively used as neutron shielding chemicals and control rods during nuclear power generation.
- We used boric powder widely in the carrom board.
- Boric acid can be used in the preservation of food grains like wheat and rice from insecticides mainly cockroaches.